Compensated Unilateral Peripheral Vestibular Loss
Age at test 62 |
||
| |
||
| Key Signs: | ||
|
When the patient illustrated above is retested 3 months after the onset of the deficit,
the question will be if there improvement is sufficient to permit the patient to work
normally and if not the focus of continued rehabilitation. A clear improvement for the
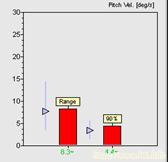
task of standing eyes closed on foam (see traces below) with reduction of pitch velocity
to within the normal range (see columns at end of traces). Remaining deficit is excessive
trunk roll when standing on 1 leg and when walking up and down stairs. Also trunk pitch
while walking with head movements (pitching of head) has a value on the borderline of normal. Standing on two legs, eyes closed, on foam. 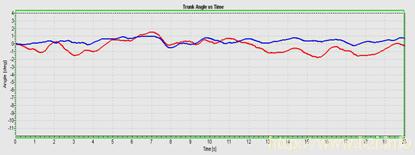
|
||
| Summary Data: | ||
|
Shows that stance control has improved considerably compared to the acute situation,
how-ever walking up stairs is still abnormal. The sensory analysis indicates the
increased use of visual inputs to control trunk sway. The summary also suggests
rehabilitation should concen-trate on improving balance control during gait tasks
with head movements or walking over obstacles, especially if this aspect is crucial
during work performance.
|
||
| Index: | ||
Indicates an improvement
in balance control compared to the acute status 3 months earlier.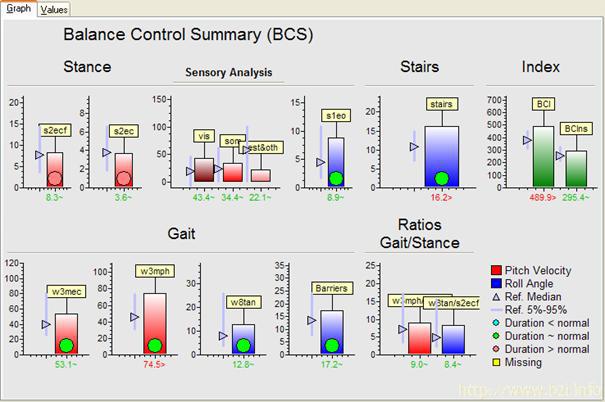
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
| [Installation] [Download] [Manual] [Reporting] [Publications] [Stance Tests] [Gait Tests] [About] |
|
|
| ©
2004-2012 Balance International Innovations GmbH 15.11.2012 |